






 degree of heat72
degree of heat72
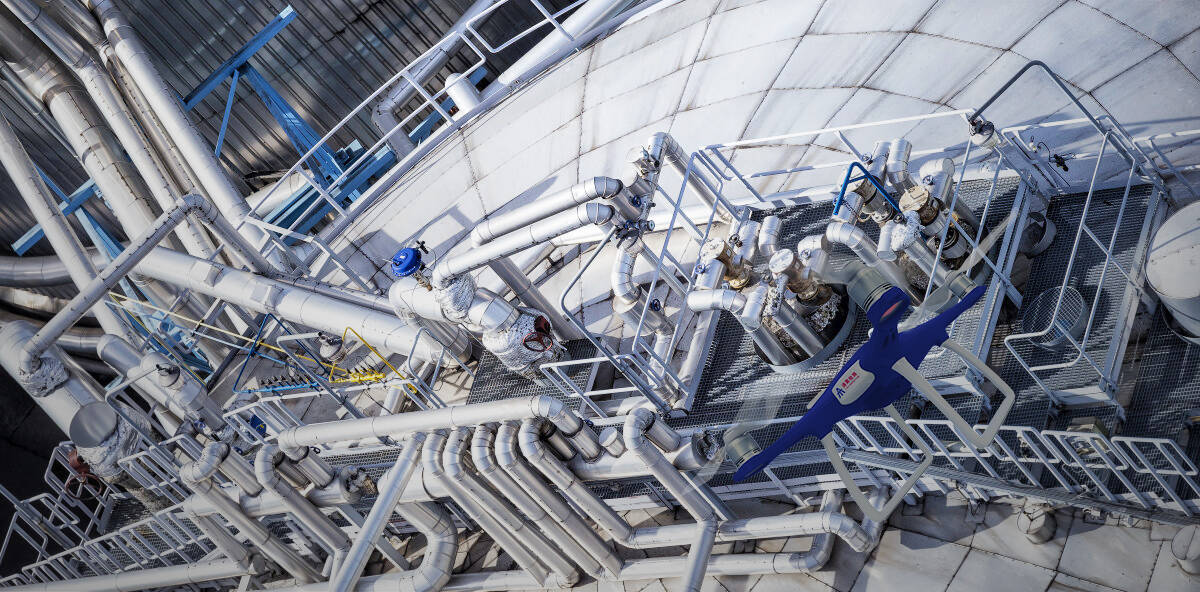
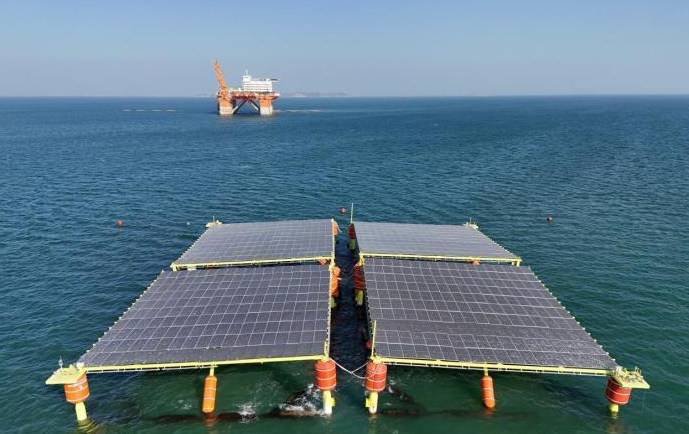
Recently, on the "Pengbo", China's largest shallow-water floating production, storage, and offloading (FPSO) facility, more than 100 photovoltaic (PV) panels have come to life, harnessing the power of sunlight to generate nearly 90,000 kilowatt-hours of "green" electricity annually. This solar power generation project on the "Pengbo" follows the implementation of CNOOC's first mixed-flow turbine power generation project in Penglai Oilfield last year, representing another milestone in green energy integration and utilization. It is also the first and largest offshore photovoltaic building integration project undertaken by CNOOC in China.

Photovoltaic building integration (PVBI) is a technology that integrates solar power generation products into building components. Unlike traditional solar PV systems attached to buildings, PVBI components serve both as energy producers and building materials. The implementation of the "Pengbo" solar power project not only endows the PV components with rainproof, sunscreen, thermal insulation, and noise reduction capabilities for offshore facilities, but also maximizes the utilization of limited space to further promote the widespread adoption of distributed green energy sources.
The "Pengbo" FPSO boasts six high-voltage power transformers distributed across its rooftops, providing electricity to critical equipment such as low- and medium-pressure compressors and water injection pumps. Solar PV panels have been added to the facility's rooftops and gunwales on the D-level living quarters, leveraging the advantages of PVBI in terms of green energy savings, material conservation, and space efficiency.
Composed of 147 monocrystalline silicon double-sided double-glass high-efficiency modules, two inverters, and one grid-connected cabinet, the project covers an installation area of approximately 320 square meters. Operating on a segmented generation and centralized grid-connection model, it enjoys the benefits of solar energy, generating 92,100 kilowatt-hours of green electricity annually. At its peak, the generated electricity can power over a thousand fluorescent lamps, resulting in a significant reduction of approximately 81 tons of carbon dioxide emissions per year.
The successful implementation of the "Pengbo" PVBI project serves as a valuable reference for future solar power projects. To date, solar power projects in Penglai Oilfield have accumulated an installation area of approximately 800 square meters, generating over 470 kilowatt-hours of green electricity daily.